Why learn different variations of the chords? As an example, think of a two chord song. You can add interest to the song by using different forms of those two chords. Even in more complex songs, it may still be useful to change to a different form of a chord from one bar to the next. (Here's a good video demonstrating switching between alternate forms of G and C.)
Here are some examples of some alternative fingerings for a couple of common chords:
(I especially like the 0454 form of A7. Think of the main chords in the key of D: D, G, and A7. When changing from G to A7, you just have to slide your fingers 2 frets up the fretboard.)
How does one figure out different chord variations? I've put together a couple of charts to help me come up with different fingerings. You can always learn the patterns for barred chords. However, if a chord includes one or more of G, C, E, or A, these charts can help you find easy alternatives using open strings. You can download the charts from here.
The first chart lists the notes for many of the chords we use. The notes are identified by Roman numerals. If you haven't seen that notation, just think of the notes by their other names: do, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti, and do. For example, a major chord consists of three notes: I, III, and V. (Or do, mi, and sol.)
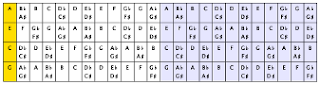
The second chart represents the notes on a ukulele fretboard. The notes shaded in yellow are the notes of the open strings. The white area is for the notes on a standard soprano ukulele. The other notes (blue) represent notes found on bigger ukuleles, as well as an additional extension for convenience so you can see full octaves on the chart, even for the key of G#.
After printing out these charts, fold over the top edge of the second page (or cut it off) so that the top of the page is the edge of the fret board. The idea is that you can place the fretboard chart over the chart of chords and have columns line up.
How does this work? As an example, let's say you want to find a fingering for the Am7 chord. Line up the fretboard chart with the "min7" row on the chord chart. The root note of Am7 is A, and so line up the I column with an A on the top line of the fretboard. You can now read off the notes of the chord: A, C, E, and G. You'll recognize these as the open notes of all four ukulele strings. But let's find an alternative so your left hand has something to do.
The next step is trickier. We must now find A, C, E, and G from different places on the fretboard. It's really guesswork at this point, but let's start with the C at the 5th fret of the G string. We're now left with the task of finding A, E, and G. We see an E at the 4th fret of the C string and a G at the 3rd fret of the E string, leaving us with an open A. These notes are all close together, making the 5430 a really easy way to form the Am7. (Since discovering this form of Am7, I seem to be using it a lot!)
Some notes: First, note that what is commonly called the "diminished" chord is really a "diminished 7th". The row labeled "dim" is the true diminished chord, and not the diminished 7th. Second, the keen observer will note that the 9th chords have five notes. Since the ukulele only has four strings, you need to delete one of the notes. Usually, the III or V is omitted.
I always enjoy finding interesting chord alternatives. I hope you find these charts as useful as I do.
Cheers! Hans